Weather and Climate
Meteorological and Weather Forecasting - P1
Organization and Structure of Meteorological Services Global Meteorological Service and Its Implications for Maritime Traffic. Weather forecasting is only possible when insights into it come from large...
Typical atmospheric parts and weather in them - P2
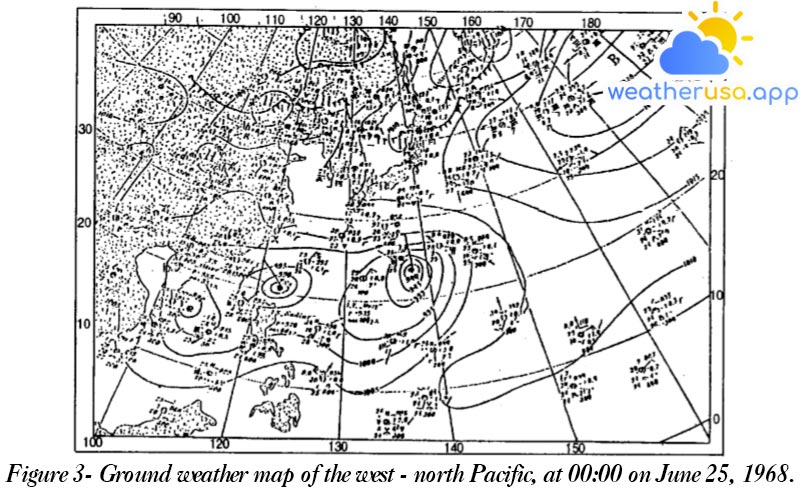
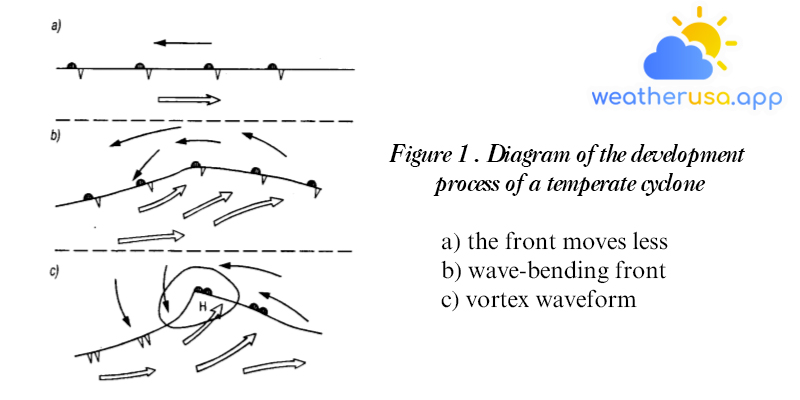
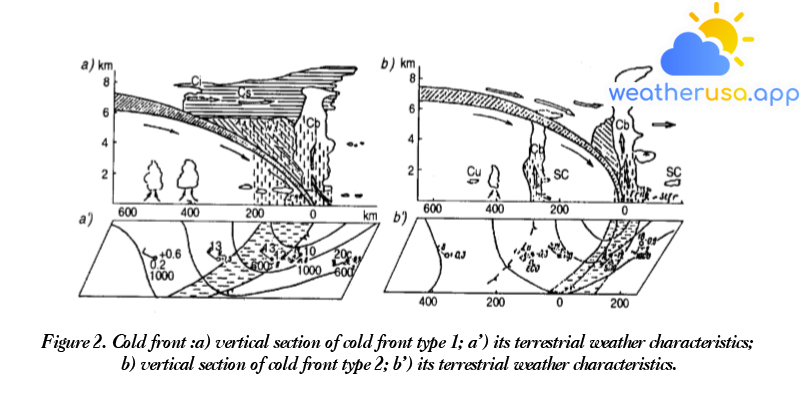
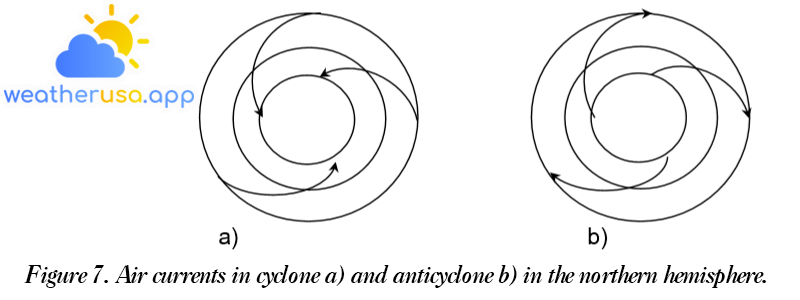
Tornadoes forward Knowledge of tornadoes This section describes in more detail the many aspects of cyclones, their formation, and development at mid and high latitudes, commonly known as temperate cyclones, or simply cyclones, and...
Typical atmospheric parts and the weather in them - P1
Weather concept What is the weather? The state of the atmosphere on the earth’s surface at a given time, at a particular place, is characterized by a set...
Meteorological prediction
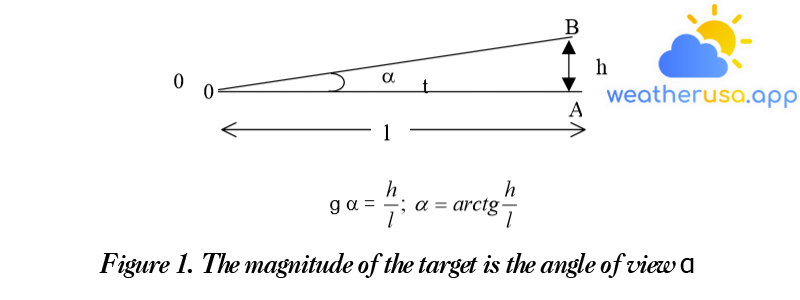
The concept of farsightedness Farsight is the ability to distinguish distant targets. It is essential to differentiate between day vision and night vision because different reasons cause the two. Factors that...
MEASUREMENT OF WIND FACTORS
MEASUREMENT OF WIND FACTORS The wind is characterized by two factors, direction, and speed In meteorology, wind direction is recognized as the wind’s direction. Wind direction can be measured in degrees or one of 16...
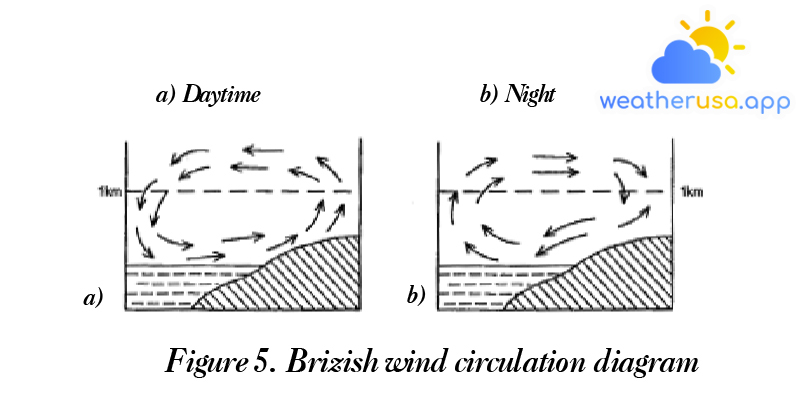
Wind and atmospheric air currents
Wind and atmospheric air currents The general concept of wind The wind is the horizontal movement of air relative to the ground. In the earth’s atmosphere, air can move in any...
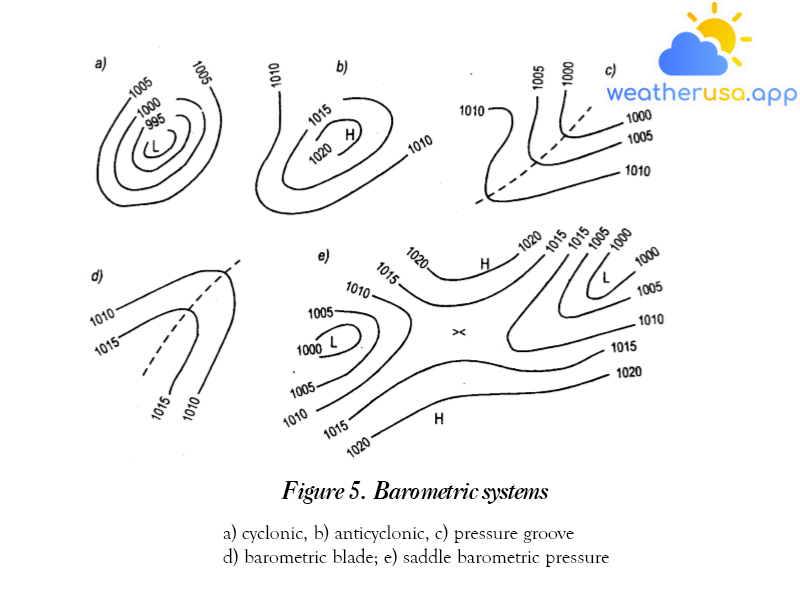
Air pressure
Air pressure Air density and pressure Air density is its amount per unit volume in g/cm3 or kg/m3. Air density depends on temperature, humidity, and barometric pressure. The physical laws of...
Precipitation
Precipitation Precipitation classification Precipitation: is the name for water in liquid or solid form falling from clouds to the ground in rain, snow, or hail.
Water in the atmosphere
Water in the atmosphere Evaporation of water Source of water vapor in the atmosphere. Water in the atmosphere can be seen in 3 states the invisible vapor state,...
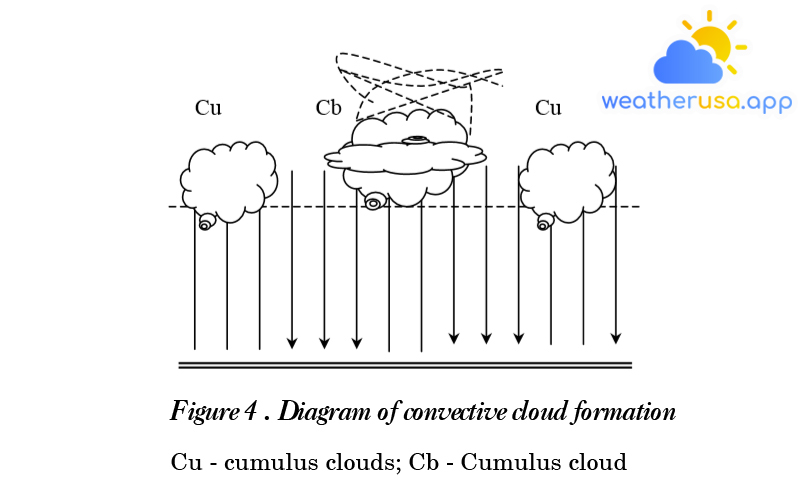
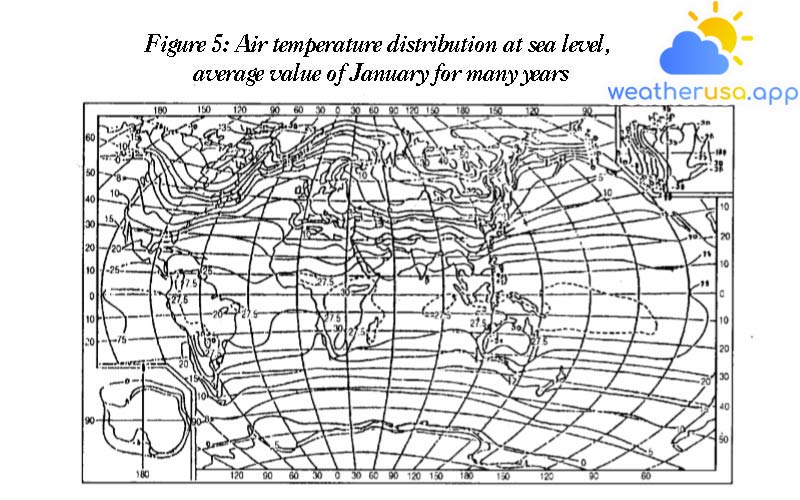
Thermal events in the atmosphere
Thermal events in the atmosphere Thermal state of the atmosphere Origin of Heat: The primary energy source for almost all atmospheric processes and events is solar heat reaching the atmosphere and...