Climate Change Indicators
Ice Breakup in Three Alaskan Rivers
Ice Breakup Ice breakup is when ice cover, found on rivers, lakes, and seas, breaks up and melts in the spring or summer. This process is a natural occurrence that occurs yearly as the weather...
Snowfall
Snowfall Snowfall is a type of precipitation in which snowflakes fall from the sky and accumulate on the ground. It typically occurs when the temperature is cold enough for the water vapor in the air to freeze into ice crystals, which then fall to the ground and form...
Snow Cover
Snow cover Snow cover refers to the extent to which a region is covered by snow. This can include snow on the ground and snow that is still falling or has recently fallen. Snow cover is an essential factor in many ecosystems, as it can affect the availability...
Snowpack
Snowpack Snowpack forms from layers of snow that accumulate in geographic regions and high elevations where the climate includes cold...
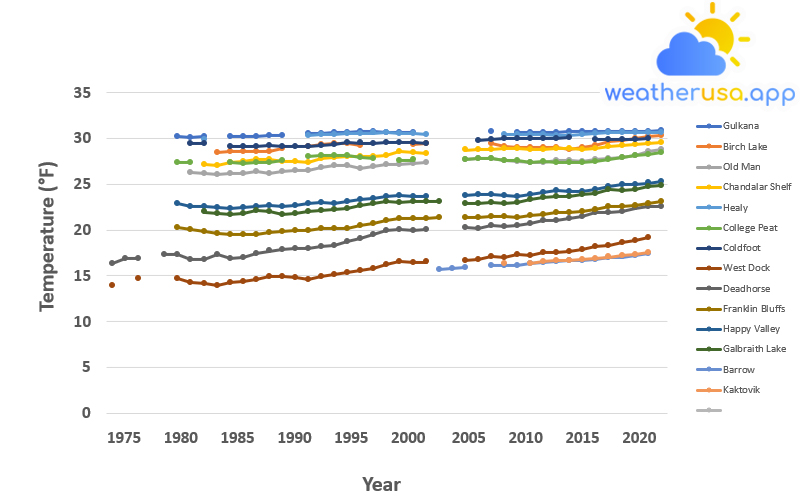
Permafrost
Permafrost Permafrost is the ground on land or under the ocean that stays below 0 °C continuously for two or more years. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, about 15% of the Northern Hemisphere, or 11% of the global surface, is covered by permafrost with a total area of about 18...
Freeze-Thaw Conditions
Freeze-Thaw Conditions Freeze-thaw refers to freezing and thawing, typically concerning weather and natural phenomena. When water freezes, it expands and can cause damage to materials and structures. When the temperature rises and the water thaws,...
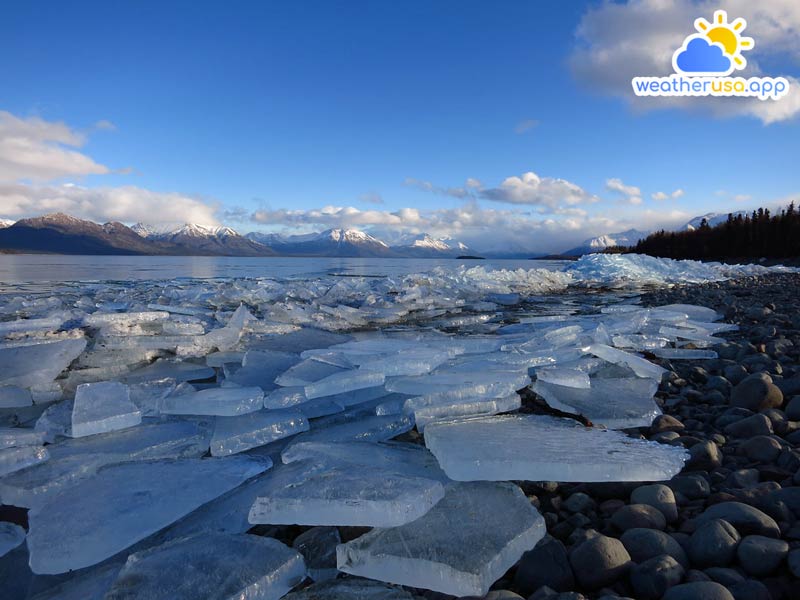
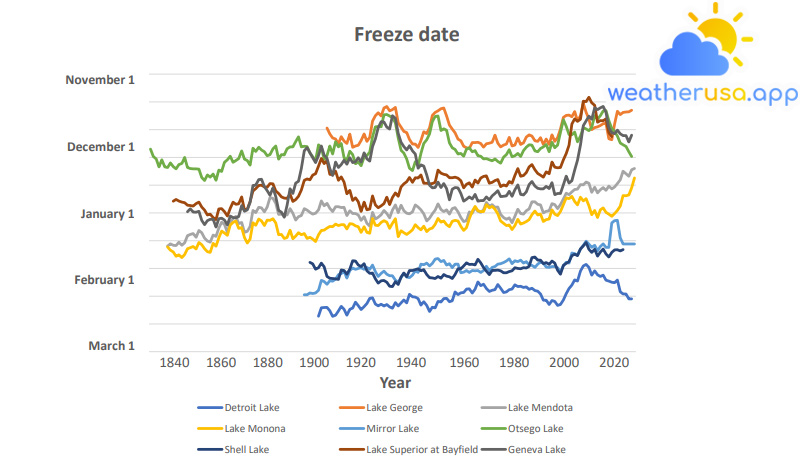
Lake Ice
Climate Change Indicators: Lake Ice Lake ice refers to the frozen surface layer of a lake. It forms when the lake’s water temperature drops below the freezing point and the surface freezes. The thickness of the lake ice can...
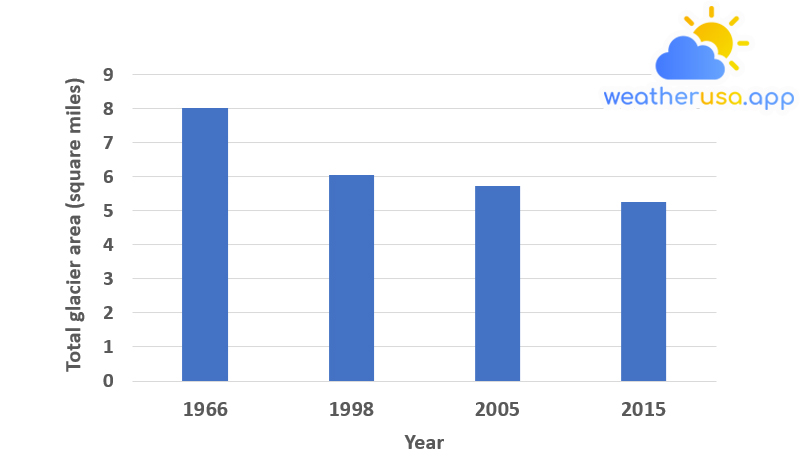
Glaciers in Glacier National Park
A Closer Look: Glaciers in Glacier National Park Figure 1. Total Glacier Surface Area in Glacier National Park, 1966–2015
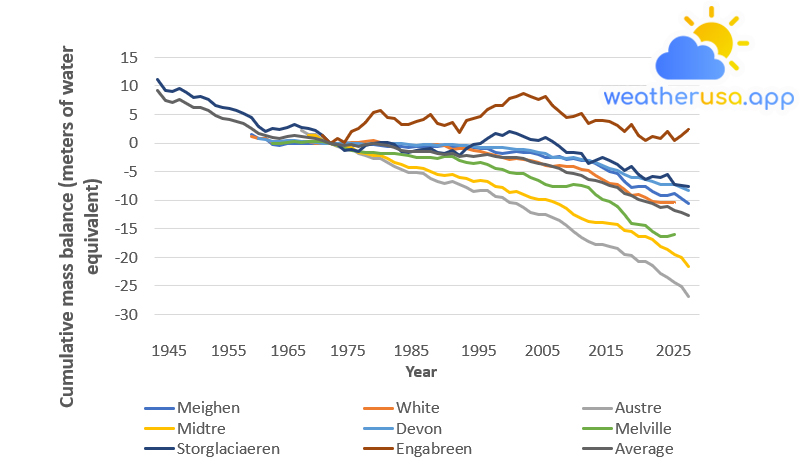
Arctic Glaciers
Climate Change Indicators: Arctic Glaciers This indicator shows the cumulative change in the mass balance of Arctic glaciers. Figure 1. Cumulative Mass Balance of Eight Arctic Glaciers,...
Glaciers
Glaciers A glacier is a persistent body of dense ice constantly moving under its weight. A glacier forms when snow accumulation exceeds its ablation for many years, often centuries. It acquires distinctive characteristics, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and...